4D time resolved SSL Unet
A Self supervised Unet architecture that can handle 3D + time data.
Overview
The 4D Upper Airway Segmentation project aims to segment the 3D plus time upper airway speech sequences from multiple subjects. In this study, subjects pronounce vowels such as “a”, “e”, “i”, “o”, and “u”. To achieve accurate segmentation, we utilize a UNet-based Vision Transformer models with self supervised training. For the SSL pre-training with proxy task, we have used the French speaker dataset. After pre-trianing the network is re-trained with data collected from university of iowa research MRI scanner.
Model Architecture
Given below figure represents the model architecture used for this project. The pre-training is done by doing proxy tasks with the French speaker dataset, and the downstream task will be to segment the airway from the newly collected data.
The architecture is based on a UNet combined with a Vision Transformer (ViT) backbone. This hybrid architecture leverages the strengths of both UNet for spatial features extraction and ViT for capturing long-range dependencies in the data.
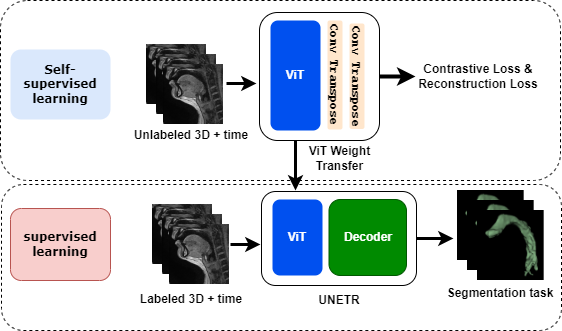
The model consists of:
- Encoder: The encoder uses a Vision Transformer to capture context and relationships within the input sequences efficiently.
- Bottleneck: A UNet-style bottleneck that combines the features extracted from the encoder before passing them to the decoder.
- Decoder: The decoder reconstructs the segmentation maps from the features, utilizing skip connections from the encoder to maintain spatial resolution.
- Output Layer: A final convolutional layer outputs the segmentation mask, indicating the segmented regions of the upper airway.
This architecture facilitates both high-level feature extraction and enabling precise segmentation of the upper airway over the 4D temporal data.
Key Features
- Convolutional Layers: Capture spatial features from 3D inputs.
- LSTM Layers: Integrate temporal information, allowing the model to learn dependencies over time sequences.
- Skip Connections: Enable better gradient flow and help in preserving spatial features across layers.
Citations
Please cite the following papers if you are using our code or dataset for development:
Airway segmentation in speech MRI using the U-net architecture
Multimodal dataset of real-time 2D and static 3D MRI of healthy French speakers